 Namespace
Namespace
Namespace is a logical grouping of flows.
Namespaces are used to organize workflows and manage access to secrets, task defaults and variables.
You can think of a namespace as a folder for your flows. Similar to folders on your file system, namespaces can be used to organize flows into logical categories. Similar to filesystems, namespaces can be indefinitely nested.
If you're looking to completely isolate environments with their own resources on the same Kestra instance, you should look at Tenants that are part of the Enterprise Edition.
Hierarchical structure when using nested namespaces
Using the dot . symbol, you can add a hierarchical structure to your namespaces which allows you to logically separate environments, projects, teams and departments. This way, your product, engineering, marketing, finance, and data teams can all use the same Kestra instance, while keeping their flows organized and separated. Various stakeholders can have their own child namespaces that belong to a parent namespace grouping them by environment, project, or team.
Namespace name
A namespace name can be built from alphanumerical characters, optionally separated by .. The hierarchy depth for namespaces is unlimited. Here are some examples of namespaces:
project_onecompany.project_twocompany.team.project_three
Using namespaces to organize flows and files
When you create a flow, you can assign a namespace to it:
id: hello_world
namespace: company.team
tasks:
- id: log_task
type: io.kestra.plugin.core.log.Log
message: hi from {{ flow.namespace }}
Note: Once you've saved your flow, you won't be able to change its namespace. You'll need to make a new flow in order to change the namespace.
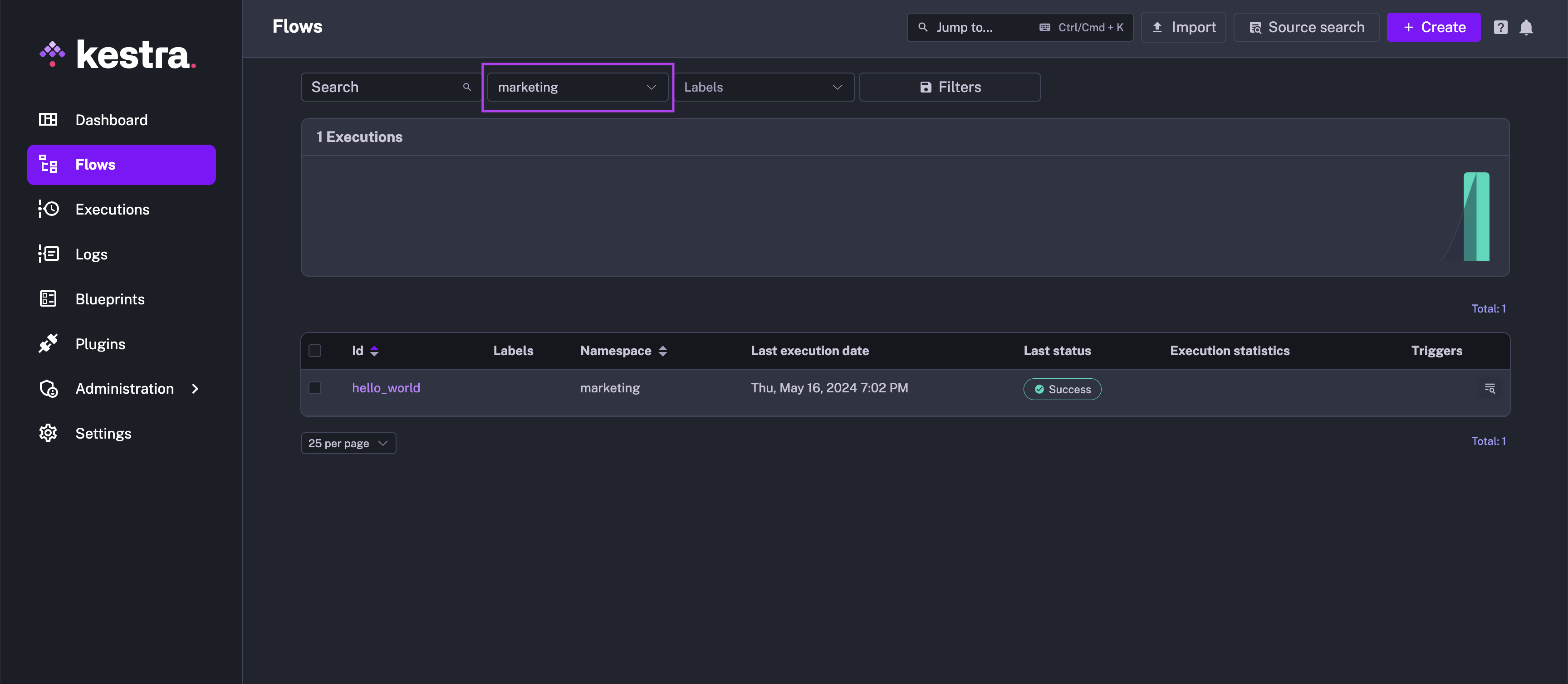
Here, the flow is assigned to the marketing namespace. This assignment of a namespace to a flow already provides a benefit of improved organization and filtering:
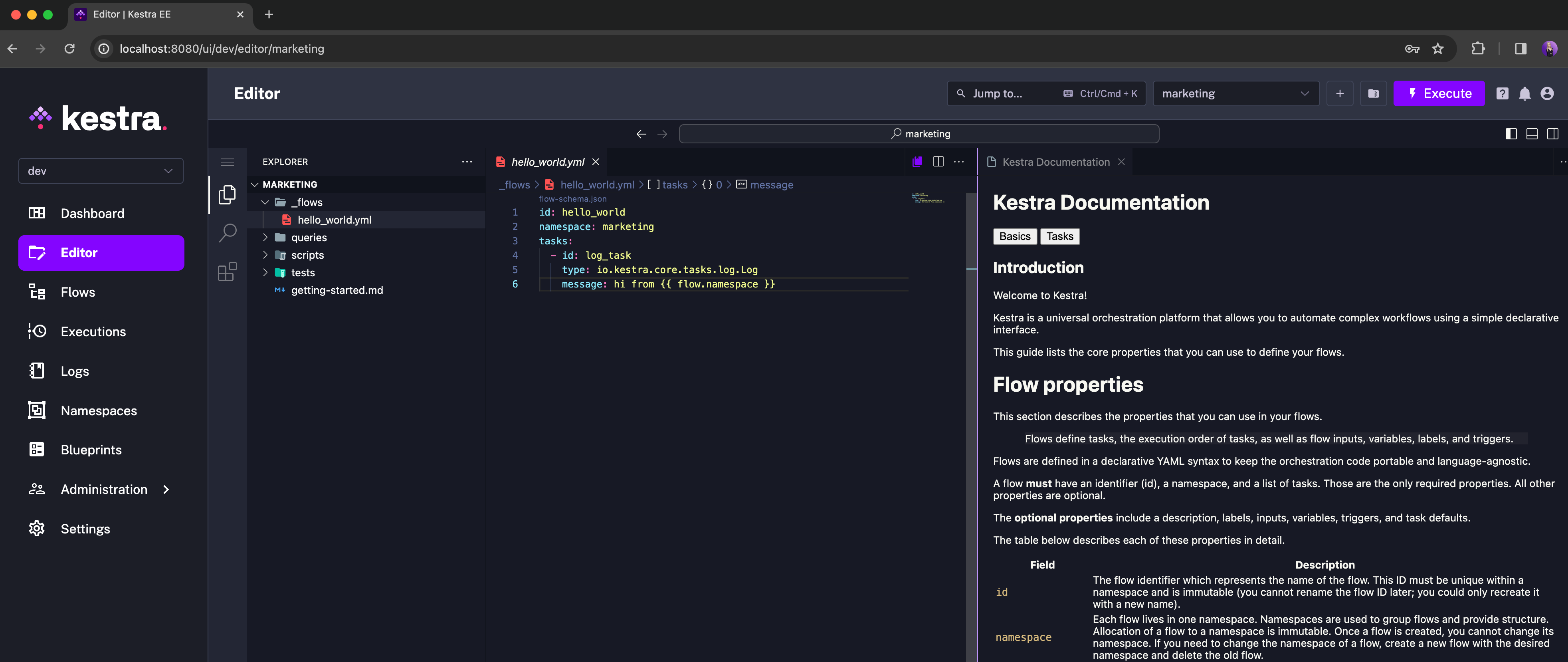
Additionally, you can organize your code on a namespace-level using the embedded Code editor and Namespace Files, with the option to sync those files from Git:
Was this page helpful?